生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 2393-2402.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.12.014
收稿日期:2022-04-02
出版日期:2022-12-18
发布日期:2023-02-15
通讯作者:
*罗辑(1960年生),研究员,研究方向为山地生态与环境。E-mail: luoji@imde.ac.cn作者简介:杨丹荔(1992年生),讲师,博士研究生,研究方向为山地生态与环境。E-mail: yangdanli5203@163.com
基金资助:
YANG Danli1( ), LUO Ji2,*(
), LUO Ji2,*( ), JIA Longyu2,3, CHEN Yunfei1
), JIA Longyu2,3, CHEN Yunfei1
Received:2022-04-02
Online:2022-12-18
Published:2023-02-15
摘要:
为探究铅在中低纬高山地区生态系统中的累积分配过程及百年时间尺度上的污染记录,以海螺沟冰川退缩区形成的完整且连续的原生演替序列为载体,通过调查植被生物量、土壤容重和厚度,测定铅在植被和土壤中的含量,系统地研究1890—2017年来铅在该原生演替序列生态系统中的贮量变化及分配格局并反演该时期铅的污染历史。结果表明:(1)各冰川退缩时期土壤中铅的含量高于背景值并表现出明显的表层富集,且表层土壤的富集系数表明土壤O层中铅含量的变化主要受外源性因素的影响而非成土母质;(2)各优势乔木不同部位铅的含量均表现为地下部分>地上部分,且地上部分的运移能力较低,而地下部分的富集程度均高于地上部分,使得根系所吸收的铅可能大部分被存留在根系组织中,导致细根中铅的含量明显高于其他部位;(3)在林下植被中,地被层(苔藓)的铅含量明显高于灌木层和草本层,具有较强的铅富集能力;(4)乔木层生物量在植被中占比最高,使其成为活体植被中最大的铅贮存单元,但地被层(苔藓)的生物量对总生物量贡献不足5%,其对植被铅的积累贡献最大可达36%,这对高山高寒地区的生态系统可能造成潜在的铅污染;(5)海螺沟冰川退缩区原生演替生态系统铅的贮量经历了从无到有的积累过程,从64.64 kg?hm?2增长到227.16 kg?hm?2,且土壤是生态系统铅的主要贮存单元;(6)生态系统铅的积累速率在1958—1970年和1980—2000年较快,并与贡嘎山东坡树轮中铅含量的变化相对应,说明海螺沟冰川退缩区原生演替序列生态系统铅的积累过程能反演近百年来铅的污染历史。
中图分类号:
杨丹荔, 罗辑, 贾龙玉, 陈云飞. 海螺沟冰川退缩区原生演替生态系统中铅累积的历史记录[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2393-2402.
YANG Danli, LUO Ji, JIA Longyu, CHEN Yunfei. Historical Records of Pb Accumulation in Primary Succession Ecosystem of Hailuogou Glacier Retreat Area[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2393-2402.
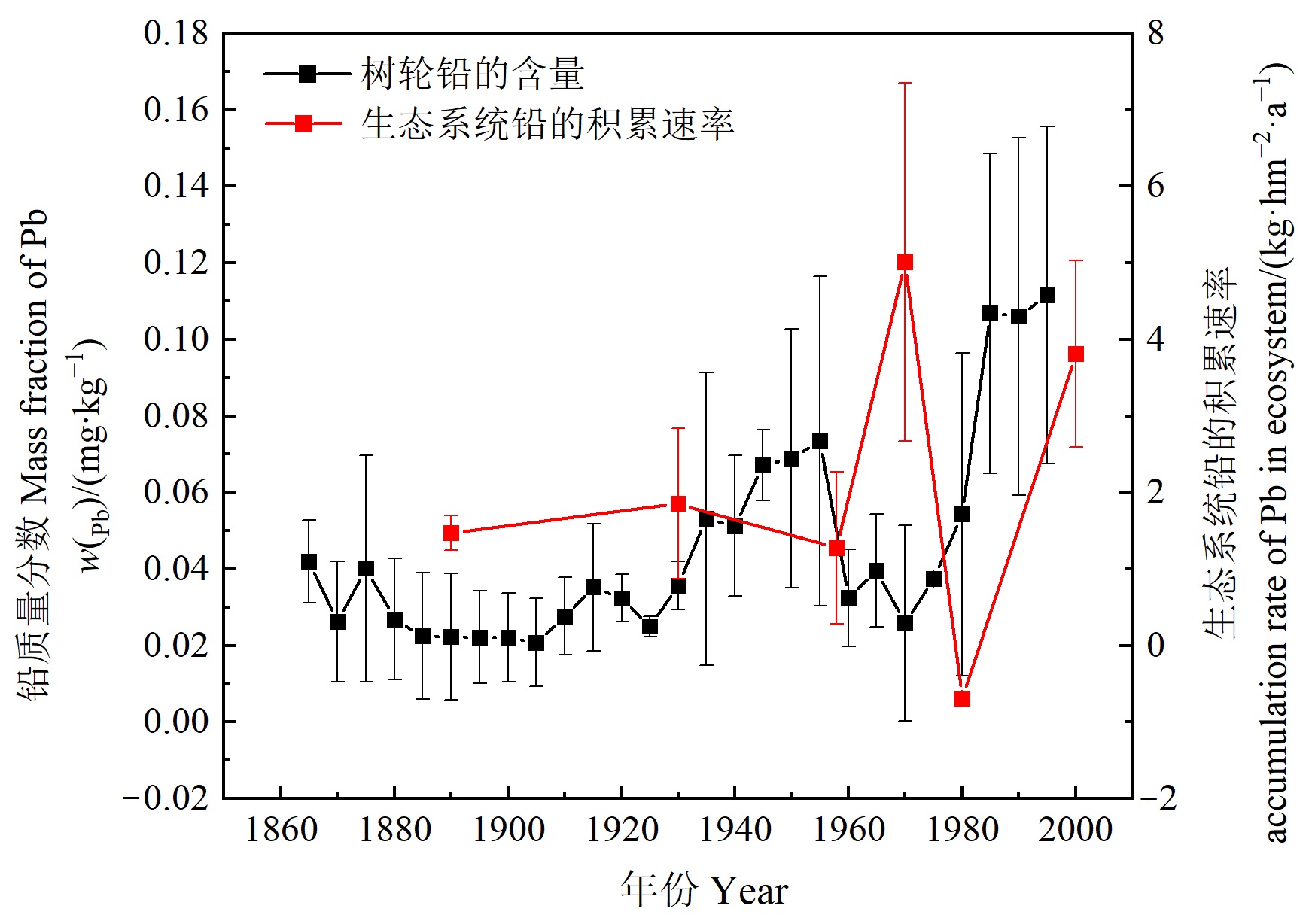
图7 生态系统铅的贮量与树轮铅质量分数 图中树轮铅含量的数据来自何咏梅等(2021)
Figure 7 Pb storage in ecosystem and mass fraction of Pb in tree rings The Pb concentration data of tree ring in this figure is from He et al. (2021)

图8 海螺沟冰川退缩区大气轨迹图 (a)—(l)为海螺沟冰川退缩区2021年1—12月的大气轨迹图
Figure 8 Atmospheric trajectory of Hailuogou Glacier Retreat area (a)?(l) were the atmospheric trajectory map of Hailuogou Glacier Retreat area from January to December in 2021
| [1] |
ALLEY R B, 2010. Reliability of ice-core science: Historical insights[J]. Journal of Glaciology, 56(200): 1095-1103.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ALOUPI M, ANGELIDIS M, 2001. Geochemistry of natural and anthropogenic metals in the coastal sediments of the island of Lesvos, Aegean Sea[J]. Environmental Pollution, 113(2): 211-219.
PMID |
| [3] | BACON K L, BAIRD A J, BLUNDELL A, et al., 2017. Questioning ten common assumptions about peatlands[J]. Mires and Peat, 19(12): 1-23. |
| [4] | BING H J, WU Y H, ZHOU J, et al., 2014. Atmospheric deposition of lead in remote high mountain of eastern Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Atmosphere Environment, 99: 425e435. |
| [5] |
BING H J, WU Y H, ZHOU J, et al., 2016. Historical trends of anthropogenic metals in Eastern Tibetan Plateau as reconstructed from alpine lake sediments over the last century[J]. Chemosphere, 148: 211-219.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
BOUTRON C F, GORLACH U, CANDELONE J P, et al., 1991. Decrease in anthropogenic lead, cadmium and zinc in Greenland snows since the late 1960s[J]. Nature, 353(6340): 153-156.
DOI URL |
| [7] | FANCOIS D V, LAËTITIA G, CATHERINE G, et al., 2007. Atmospheric lead and heavy metal pollution records from Belgian peat bog spanning the last two millenia: human impact on a regional to global scale[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 337(2-3): 282-295. |
| [8] |
FARMER J G, EADES L J, MACKENZIE A B, et al., 1996. Stable lead isotope record of lead pollution in Loch Lomond sediments study 1630 AD[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 30(10): 3080-3083.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
FU X W, FENG X N, WANG S F, et al., 2009. Temporal and spatial distributions of total gaseous mercury concentrations in ambient air in a mountainous are in southwestern China: implications for industrial and domestic mercury emission in remote areas in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 407(7): 2306-2314.
DOI URL |
| [10] | GLOVER L J, EICK M J, BRADY P V, 2002. Desorption kinetics of Cadmium and lead from goethite: influence of time and organic acids[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 66(3): 797-804. |
| [11] |
GOLOMB D, RYAN D, EBY N, et al., 1997. Atmospheric deposition of toxics onto Massachusetts Bay-I[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 31(9): 1349-1359.
DOI URL |
| [12] | KABATA-PENDIAS, 2000. Trace elements in soils and plants[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press. |
| [13] |
KYLLÖNEN K, KARLSSON V, RUOHO-AIROLA T, 2009. Trace element deposition and trends during a ten-year period in Finland[J]. Science Total Environment, 407(7): 2260-2269.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LUO J, SHE J, YANG P J, et al., 2014. Heavy metal concentrations in timberline trees of eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Ecotoxicology, 23(6): 1086-1098.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
LUO J, TANG R G, SUN S Q, et al., 2015. Lead distribution and possible sources along vertical zone spectrum of typical ecosystems in the Gongga Mountain, eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 115: 132-140
DOI URL |
| [16] |
NDZANGOU S O, RICHER-LAFLECHE M, HOULE D, 2005. Sources and evolution of anthropogenic lead in dated sediments from Lake Clair, Quebec, Canada[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34(3): 1016-1025.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
PADILLA K L, ANDERSON K A, 2002. Trace element concentrations of tree-rings biomonitoring centuries of environmental change[J]. Chemoshpere, 49(6): 575-585.
DOI URL |
| [18] | PAN Y P, WANG Y S, 2015. Atmospheric wet and dry deposition of trace elements at 10 sites in Northern China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15(2): 951-972. |
| [19] |
RENBERG I, BRANNVALL M L, BINDLER R, et al., 2002. Stable lead isotopes and lake sediments: A useful combination for the study of atmospheric lead pollution history[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 292(1-2): 45-54.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ROSMAN K, CHISHOLM W, BOUTRON C, et al., 1993. Isotopic evidence for the source of lead in Greenland snows since the late 1960s[J]. Nature, 362(6418): 333-335.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SCHWIKOWSKI I, BARBANTE C, DOERING T, et al., 2004. Post-17th-century changes of European lead emission recorded in high-altitude alpine snow and ice[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(4): 957-964.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SPOKES L J, JICKELLS T D, 1995. Factor controlling the solubility of aerosol trace metals in the atmosphere and on mixing into seawater[J]. Aquatic Geochemistry, 1: 355-374.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
STANKOVIC J D, SABOVLJEVIC A D, SABVLJEVIC M S, 2018. Bryophytes and heavy metals: A review[J]. Acta Botanica Croatica, 77(2): 109-118.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
TANG R G, LUO J, SHE J, et al., 2015. The cadmium and lead of soil in timberline coniferous forests, eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(1): 303-310
DOI URL |
| [25] |
TANG R G, LUO J, YANG P J, et al., 2014. Trace metals of needles and litter in timberline forests in the eastern of Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 45: 669-676.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
TYLER G, 1990. Bryophytes and heavy-metals-a literature- review[J]. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 104(1-3): 231-253.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
UZU G, SOBANSKA S, SARRET G, et al., 2010. Foliar lead uptake by lettuce exposed to atmospheric fallouts[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(3): 1036-1042.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WANG X, LUO J, LIN C J, et al., 2020a. Elevated cadmium pollution since 1890s records by forest chronosequence in deglaciated region of Gongga, China[J]. Environment Pollution, 260: 114082.
DOI URL |
| [29] | WANG X, LUO J, YUAN W, et al., 2020b. Global warming accelerates uptake of atmospheric mercury in regions experiencing glacier retreat[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(4): 2049-2055. |
| [30] |
WANG X, YUAN W, FENG X B, et al., 2019. Moss facilitating mercury, lead and cadmium enhanced accumulation in organic soils over glacial erratic at Mt. Gongga, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 254(Part A): 112974.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 陈英旭, 林琦, 陆芳, 等, 2000. 有机酸对铅、镉植株危害的解毒作用研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 20(4): 467-472. |
| CHEN Y X, LIN Q, LU F, et al., 2000. Study on detoxication of organic acid to raddish under the stress of Pb and Cd[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 20(4): 467-472. | |
| [32] | 陈文德, 彭培好, 李贤伟, 2009. 岩-土-植系统中重金属的迁聚规律研究[J]. 土壤通报, 40(2): 370-373. |
| CHEN W D, PENG P H, LI X W, 2009. The transportation and accumulation characteristics of heavy metal in rock-soil-plant system[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 40(2): 370-373. | |
| [33] | 董林林, 赵先贵, 巢世军, 等, 2008. 镉污染土壤的植物吸收与修复研究[J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 24(3): 292-295, 299. |
| DONG L L, ZHAO X G, CHAO S J, et al., 2008. Study on plants absorbing and phytoremediation of Cd polluted soil[J]. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 24(3): 292-295, 299. | |
| [34] | 段德超, 于明革, 施积炎, 2014. 植物对铅的吸收、转运、累积和解毒机制研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(1): 287-296. |
| DUAN D C, YU M G, SHI J Y, 2014. Research advances in uptake, translocation, accumulation and detoxification of Pb in plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(1): 287-296. | |
| [35] | 何咏梅, 罗辑, 李伟, 等, 2021. 基于年轮年代学重建青藏高原东缘百年来重金属污染历史[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 30(1): 191-201. |
| HE Y M, LUO J, LI W, et al., 2021. Reconstruction of heavy metal deposition history in the eastern margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on ring chronology[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtza Basin, 30(1): 191-201. | |
| [36] | 霍文冕, 姚檀栋, 李月芳, 等, 1999. 7000 m处冰芯中Pb记录揭示人类活动污染在加剧[J]. 科学通报, 44(9): 978-981. |
| HUO W M, YAO T D, LI Y F, et al., 1999. Pb records in ice cores at 7000 m reveal that human activity pollution is increasing[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(9): 978-981. | |
| [37] | 李真, 姚檀栋, 田立德, 等, 2006. 慕士塔格冰芯记录的近50年来大气中铅含量变化[J]. 科学通报, 51(15): 1833-1836. |
| LI Z, YAO T D, TIAN L D, et al., 2006. Changes of lead content in the atmosphere recorded by Muztagh ice core in recent 50 years[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(15): 1833-1836. | |
| [38] | 潘胜强, 王铎, 吴山, 等, 2014. 土壤理化性质对重金属污染土壤改良的影响分析[J]. 环境工程, 32(增刊): 600-603, 633. |
| PAN S Q, WANG D, WU S, et al., 2014. Impact of soil properties on improvement of heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Engineering, 32(S1): 600-603, 633. | |
| [39] | 佘佳, 2014. 贡嘎山海螺沟冰川退缩区镉的生物地球化学特征[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学: 22-49. |
| SHE J, 2014. Biogeochemical characteristic of cadmium in Hailuogou glacial retreated area[D]. Beijing:University of Chinese Academy of Science: 22-49. | |
| [40] | 唐荣贵, 2015. 贡嘎山东坡垂直带典型生态系统植物与土壤铅和镉的垂直分异[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学:35-78. |
| TANG R G, 2015. The vertical differentiation of lead and cadmium in plants and soil of the typical ecosystems along the altitudinal belt in the eastern slope of the Gongga Mountain[D]. Beijing:University of Chinese Academy of Science:35-78. | |
| [41] | 王春苗, 石中山, 杨剑虹, 等, 2009. 重庆土壤铅含量污染评价及其影响因素分析[J]. 广西农业科学, 40(9): 1172-1176. |
| WANG C M, SHI Z S, YANG J H, et al., 2009. An assessment of lead content in soils and the factors influencing its accumulation in Chongqing[J]. Guangxi Agriculture Sciences, 40(9): 1172-1176. | |
| [42] | 夏时雨, 刘清, 1994. 土壤中不同形态铅的提取及其取样深度[J]. 环境污染与防治, 16(4): 27-29. |
| XIA S Y, LIU Q, 1994. Extraction and sampling depth of different forms of lead in soil[J]. Environment Pollution & Control, 16(4): 27-29. | |
| [43] | 杨丹丹, 罗辑, 佘佳, 等, 2015. 贡嘎山海螺沟冰川退缩区原生演替序列植被生物量动态[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(11): 1843-1850. |
| YANG D D, LUO J, SHE J, et al., 2015. Dynamics of vegetation biomass along the chronosequence in Hailuogou glacier retreated area, Mt Gongga[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 24(11): 1843-1850. | |
| [44] | 杨丹荔, 罗辑, 李伟, 等, 2020. 海螺沟冰川退缩区原生演替中土壤重金属的积累[J]. 地球与环境, 48(4): 424-431. |
| YANG D L, LUO J, LI W, et al., 2020. Accumulation of heavy metals in soil during primary succession in Hailuogou glacier retreat area[J]. Earth and Environment, 48(4): 424-431. |
| [1] | 王琳, 卫伟. 黄土高原典型县域生态系统服务变化特征及驱动因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1140-1148. |
| [2] | 张露, 何雨霏, 陈坦, 杨婷, 张冰, 金军. 2011—2020年汾渭平原农田生态系统碳足迹的时空格局演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1149-1162. |
| [3] | 郝蕾, 翟涌光, 戚文超, 兰穹穹. 2001-2020年内蒙古植被碳源/碳汇时空动态及对气候因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 825-834. |
| [4] | 翁升恒, 张玉琴, 姜冬昕, 潘卫华, 李丽纯, 张方敏. 福建省森林植被NEP时空变化及影响因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 845-856. |
| [5] | 许静, 廖星凯, 甘崎旭, 周茅先. 基于MSPA与电路理论的黄河流域甘肃段生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 805-813. |
| [6] | 张平江, 党国锋. 基于MCR模型与蚁群算法的洮河流域生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 481-491. |
| [7] | 朱锦维, 柯新利, 何利杰, 周婷, 王青, 任妍钰. 基于价值链理论的生态产品价值实现机制理论解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 421-428. |
| [8] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [9] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [10] | 肖国举, 李秀静, 郭占强, 胡延斌, 王静. 贺兰山东麓土壤有机碳对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1754-1764. |
| [11] | 蔡国俊, 袁桂香, 符辉. 基于文献计量分析的生态网络研究现状和趋势[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1690-1699. |
| [12] | 舒洋, 陈魁, 李航, 魏江生, 赵鹏武, 周梅. 高纬度冻土区林火干扰对土壤碳释放影响研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1278-1284. |
| [13] | 刘香华, 王秀明, 刘谞承, 张音波, 刘飘. 基于外溢生态系统服务价值的广东省生态补偿机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1024-1031. |
| [14] | 钱学诗, 李勇, 钱壮壮, 葛晓敏, 唐罗忠. 北亚热带东部次生阔叶林降水过程中的镉、铅、砷含量变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 979-989. |
| [15] | 姜鹏, 秦美欧, 李荣平, 孟莹, 杨霏云, 温日红, 孙沛, 方缘. 中国典型生态系统GPP的季节变异及其影响要素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 643-651. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
